In order to demonstrate the possibilities of the light field technology of HD Vision and rabbit AI, optically difficult objects with highly reflective materials were used for the recordings.
HD Vision Systems and rabbitAI are both specialists in the processing of light field images. Both companies have analyzed the advantages of their systems based on a test.
In recent years, light field technology has become increasingly popular as an image capture method. Its main advantage is that it can measure not only the light intensity but also the direction of the light rays that hit the sensor. This enables a much more detailed capture of the scene than conventional 2D imaging and opens up new possibilities for robotics or autonomous driving. There are numerous techniques for capturing light fields, such as a single camera capturing a scene from multiple angles, or multiple cameras capturing images from different angles, or a series of microlenses mounted in front of a digital camera sensor to capture light field information. There is still debate among experts as to which technique is best for capturing light fields, but there is no doubt that camera arrays are among the favorites.
Test comparison for point cloud processing
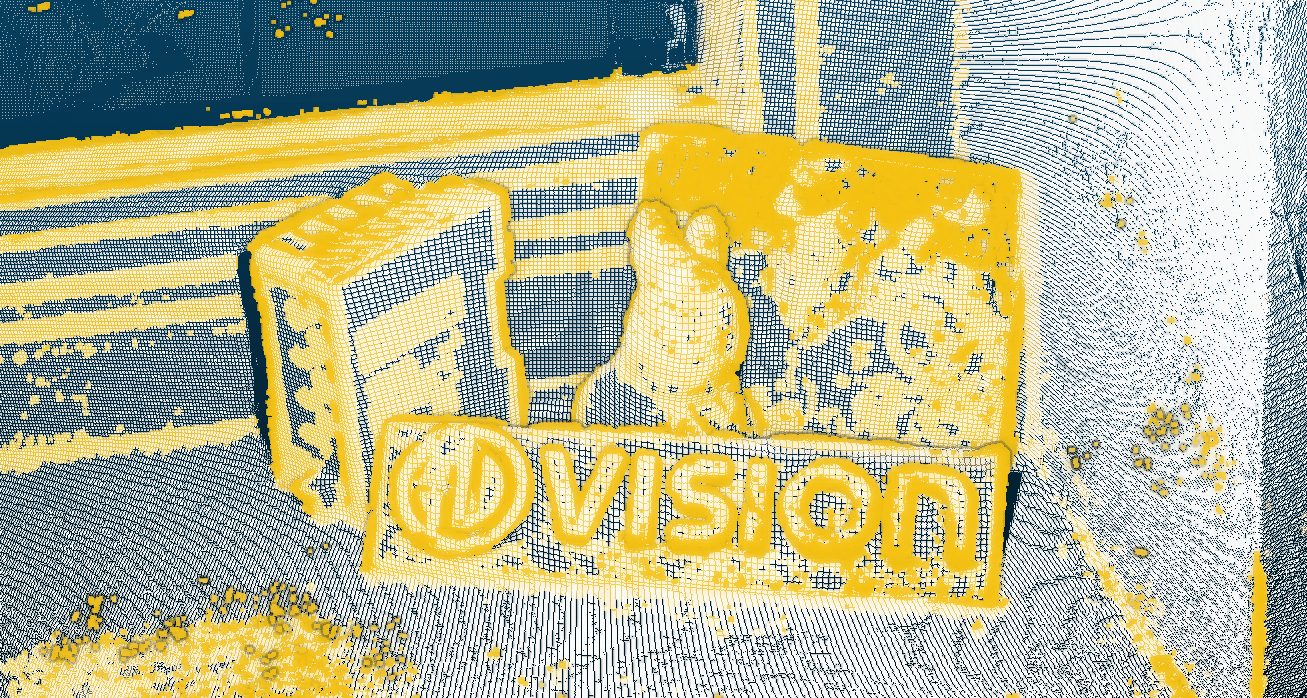
HD Vision’s solution generates 3D points at object features such as edges, i.e. where it is important for 3D recognition.

rabbitAI’s reconstruction achieves a high surface quality and a very dense reconstruction of the scenes with a higher computational effort.
The two Heidelberg-based companies HD Vision Systems and rabbitAI, which specialize in the processing of light field images, have investigated the possibilities of using 3D information from camera arrays. HD Vision Systems took a traditional physics-based approach to machine vision, while rabbitAI used a machine learning approach. ‘Like HD Vision Systems, our startup comes from the same research facility,’ explains Karsten Krispin, CEO of rabbitAI: ’We developed and analyzed the best possible scene reconstructions there. This enables a very flexible implementation that allows precise measurement statements and error estimates at the same time.’
Both companies worked with the same data (2D images) from the same sensor. The images were captured using the LumiScanX light field camera array, which consists of thirteen cameras arranged in an X-shape that capture an image scene from slightly different positions. In order to best demonstrate the possibilities of the HD Vision and rabbitAI approaches, optically difficult objects with highly reflective materials were used for the images. HD Vision Systems calibrated LumiScanX and determined the important system parameters. The images were then recorded and used to create the 3D information. This 3D information was also determined using rabbitAI’s AI approach. The resulting 3D information was compared for error deviation, coverage and qualitative impression.
It was expected that the reconstruction method of HD Vision Systems, which runs in real time, would have different properties compared to the rabbitAI approach, which requires a significantly higher overall computational effort to analyze the probabilistic model. In the subsequent evaluation, the plausible hypotheses were confirmed. The reconstruction of rabbitAI achieves a high surface quality and a very dense reconstruction of the scenes with a higher computational effort. HD Vision’s solution delivers a 3D reconstruction in textured areas. It tends to generate 3D points on object features such as edges, i.e. where it is important for 3D recognition. This enables real-time application, e.g. in the control of robotics applications with high accuracy.
Applications of both methods
HD Vision Systems’ approach is ideal for situations, such as on a production line, where time is of the essence and a thin 3D point cloud is sufficient to enable the robot to recognize, grasp and move an object to the desired location quickly and in real time. On the other hand, the denser but correspondingly more time-consuming reference data from rabbitAI can be ideally used as training data for the optimization of machine learning. The strength of the Rabbit AI solution is particularly evident in applications that are heavily PC-fixated and have to make do with inexpensive hardware (edge devices), e.g. AR/VR headsets, AD/ADAS (Advanced Driver Assistance Systems) and in cabin sensing solutions.
About rabbitAI

Zu Beginn des Jahres 2020 wurde rabbitAI mit der Mission gegründet, eine grundlegende Herausforderung auf dem Weg des maschinellen Lernens anzugehen: den Mangel an Daten.
Heute besteht ihre Tagesgeschäft darin, Szenen mit proprietären Lichtfeld-Setup aufzunehmen, aus dem sie ultrarealistische 3D-Modelle erstellen. Diese Modelle, kombiniert mit Wissen über Licht und Schatten, ermöglichen es ihnen, Trainingsdaten zu erstellen, die reale Szenarien nachahmen.



